-->
- Create Dmg For Mac Application Form
- Create Dmg For Mac Application Download
- Create Dmg For Mac Application Form
Is to create.dmg file is to share.pkg file (Package Maker). In pkg file my client want to install app without introduction, read me as well as license agreement, I removed the license and readme but unable to remove introduction section. Feb 19, 2020 create-dmg. Create a good-looking DMG for your macOS app in seconds. Imagine you have finished a macOS app, exported it from Xcode, and now want to distribute it to users. The most common way of distributing an app outside the Mac App Store is by putting it in a.dmg file. These are hard to create, especially good-looking ones.
Applies to: Configuration Manager (current branch)
Keep the following considerations in mind when you create and deploy applications for Mac computers.
Important
The procedures in this topic cover information about deploying applications to Mac computers on which you installed the Configuration Manager client. Mac computers that you enrolled with Microsoft Intune do not support application deployment.
General considerations
You can use Configuration Manager to deploy applications to Mac computers that run the Configuration Manager Mac client. The steps to deploy software to Mac computers are similar to the steps to deploy software to Windows computers. However, before you create and deploy applications for Mac computers that are managed by Configuration Manager, consider the following:
Before you can deploy Mac application packages to Mac computers, you must use the CMAppUtil tool on a Mac computer to convert these applications into a format that can be read by Configuration Manager.
Configuration Manager does not support the deployment of Mac applications to users. Instead, these deployments must be made to a device. Similarly, for Mac application deployments, Configuration Manager does not support the Pre-deploy software to the user’s primary device option on the Deployment Settings page of the Deploy Software Wizard.
Mac applications support simulated deployments.
You cannot deploy applications to Mac computers that have a purpose of Available.
The option to send wake-up packets when you deploy software is not supported for Mac computers.
Mac computers do not support Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) for downloading application content. If an application download fails, it is restarted from the beginning.
Configuration Manager does not support global conditions when you create deployment types for Mac computers.
Steps to create and deploy an application
The following table provides the steps, details, and information for creating and deploying applications for Mac computers.
| Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Prepare Mac applications for Configuration Manager | Before you can create Configuration Manager applications from Mac software packages, you must use the CMAppUtil tool on a Mac computer to convert the Mac software into a Configuration Manager.cmmac file. |
| Step 2: Create a Configuration Manager application that contains the Mac software | Use the Create Application Wizard to create an application for the Mac software. |
| Step 3: Create a deployment type for the Mac application | This step is required only if you did not automatically import this information from the application. |
| Step 4: Deploy the Mac application | Use the Deploy Software Wizard to deploy the application to Mac computers. |
| Step 5: Monitor the deployment of the Mac application | Monitor the success of application deployments to Mac computers. |
Supplemental procedures to create and deploy applications for Mac computers
Use the following procedures to create and deploy applications for Mac computers that are managed by Configuration Manager.
Step 1: Prepare Mac applications for Configuration Manager
The process for creating and deploying Configuration Manager applications to Mac computers is similar to the deployment process for Windows computers. However, before you create Configuration Manager applications that contain Mac deployment types, you must prepare the applications by using the CMAppUtil tool. This tool is downloaded with the Mac client installation files. The CMAppUtil tool can gather information about the application, which includes detection data from the following Mac packages:
Apple Disk Image (.dmg)
Meta Package File (.mpkg)
Mac OS X Installer Package (.pkg)
Mac OS X Application (.app)
After it gathers application information, the CMAppUtil then creates a file with the extension .cmmac. This file contains the installation files for the Mac software and information about detection methods that can be used to evaluate whether the application is already installed. CMAppUtil can also process .dmg files that contain multiple Mac applications and create different deployment types for each application.
Copy the Mac software installation package to the folder on the Mac computer where you extracted the contents of the macclient.dmg file that you downloaded from the Microsoft Download Center.
On the same Mac computer, open a terminal window and navigate to the folder where you extracted the contents of the macclient.dmg file.
Navigate to the Tools folder and type the following command-line command:
./CMAppUtil<properties>
For example, say you want to convert the contents of an Apple disk image file named MySoftware.dmg that's stored in the user's desktop folder into a cmmac file in the same folder. You also want to create cmmac files for all applications that are found in the disk image file. To do this, use the following command line:
./CMApputil –c /Users/<User Name>/Desktop/MySoftware.dmg -o /Users/<User Name>/Desktop -a
Note
The application name can't be more than 128 characters.
To configure options for CMAppUtil, use the command-line properties in the following table:
Property More information -h Displays the available command-line properties. -r Outputs the detection.xml of the provided .cmmac file to stdout. The output contains the detection parameters and the version of CMAppUtil that was used to create the .cmmac file. -c Specifies the source file to be converted. -o Specifies the output path in conjunction with the –c property. -a Automatically creates .cmmac files in conjunction with the –c property for all applications and packages in the disk image file. -s Skips generating the detection.xml if no detection parameters are found and forces the creation of the .cmmac file without the detection.xml file. -v Displays more detailed output from the CMAppUtil tool together with diagnostic information. Ensure that the .cmmac file has been created in the output folder that you specified.
Create a Configuration Manager application that contains the Mac software
Use the following procedure to help you create an application for Mac computers that are managed by Configuration Manager.
In the Configuration Manager console, choose Software Library > Application Management > Applications.
On the Home tab, in the Create group, choose Create Application.
On the General page of the Create Application Wizard, select Automatically detect information about this application from installation files.
Note
If you want to specify information about the application yourself, select Manually specify the application information. For more information about how to manually specify the information, see How to create applications with Configuration Manager.
In the Type drop-down list, select Mac OS X.
In the Location field, specify the UNC path in the form <server><share><filename> to the Mac application installation file (.cmmac file) that will detect application information. Alternatively, choose Browse to browse to and specify the installation file location.
Note
You must have access to the UNC path that contains the application.
Choose Next.
On the Import Information page of the Create Application Wizard, review the information that was imported. If necessary, you can choose Previous to go back and correct any errors. Choose Next to proceed.
On the General Information page of the Create Application Wizard, specify information about the application such as the application name, comments, version, and an optional reference to help you reference the application in the Configuration Manager console.
Note
Some of the application information might already be on this page if it was previously obtained from the application installation files.
Choose Next, review the application information on the Summary page, and then complete the Create Application Wizard.
The new application is displayed in the Applications node of the Configuration Manager console.
Step 3: Create a deployment type for the Mac application
Use the following procedure to help you create a deployment type for Mac computers that are managed by Configuration Manager.
Note
If you automatically imported information about the application in the Create Application Wizard, a deployment type for the application might already have been created.
In the Configuration Manager console, choose Software Library > Application Management > Applications.
Select an application. Then, on the Home tab, in the Application group, choose Create Deployment Type to create a new deployment type for this application.
Note
You can also start the Create Deployment Type Wizard from the Create Application Wizard and from the Deployment Types tab of the <application name>Properties dialog box.
On the General page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, in the Type drop-down list, select Mac OS X.
In the Location field, specify the UNC path in the form <server><share><filename> to the application installation file (.cmmac file). Alternatively, choose Browse to browse to and specify the installation file location.
Note
You must have access to the UNC path that contains the application.
Choose Next.
On the Import Information page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, review the information that was imported. If necessary, choose Previous to go back and correct any errors. Choose Next to continue.
On the General Information page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, specify information about the application such as the application name, comments, and the languages in which the deployment type is available.
Note
Some of the deployment type information might already be on this page if it was previously obtained from the application installation files.
Choose Next.
On the Requirements page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, you can specify the conditions that must be met before the deployment type can be installed on Mac computers.
Choose Add to open the Create Requirement dialog box and add a new requirement.
Note
You can also add new requirements on the Requirements tab of the <deployment type name>Properties dialog box.
From the Category drop-down list, select that this requirement is for a device.
From the Condition drop-down list, select the condition that you want to use to assess whether the Mac computer meets the installation requirements. The contents of this list varies depending on the category that you select.
From the Operator drop-down list, choose the operator to use to compare the selected condition to the specified value to assess whether the user or device meets the installation requirements. The available operators vary depending on the selected condition.
In the Value field, specify the values to use with the selected condition and operator to assess whether the user or device meets in the installation requirement. The available values vary depending on the condition and operator that you select.
Choose OK to save the requirement rule and exit the Create Requirement dialog box.
On the Requirements page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, choose Next.
On the Summary page of the Create Deployment Type Wizard, review the actions for the wizard to take. If necessary, choose Previous to go back and change deployment type settings. Choose Next to create the deployment type.
After the Progress page finishes, review the actions that have been taken, and then choose Close to complete the Create Deployment Type Wizard.
If you started this wizard from the Create Application Wizard, you will return to the Deployment Types page.
Deploy the Mac application
The steps to deploy an application to Mac computers are the same as the steps to deploy an application to Windows computers, except for the following differences:
The deployment of applications to users is not supported.
Deployments that have a purpose of Available are not supported.
The Pre-deploy software to the user’s primary device option on the Deployment Settings page of the Deploy Software Wizard is not supported.
Because Mac computers do not support Software Center, the setting User notifications on the User Experience page of the Deploy Software Wizard is ignored.
The option to send wake-up packets when you deploy software is not supported for Mac computers.
Note
You can build a collection that contains only Mac computers. To do so, create a collection that uses a query rule and use the example WQL query in the How to create queries topic.
For more information, see Deploy applications.
Step 5: Monitor the deployment of the Mac application
You can use the same process to monitor application deployments to Mac computers as you would to monitor application deployments to Windows computers.
For more information, see Monitor applications.
Learning how to create a bootable macOS installation disk can be helpful in a variety of situations. Rather than download and install a new OS from Apple's servers each time, it can be used for multiple installations on different machines. It can also help in situations where the operating system is corrupted or installation from app store shows errors.
To create a bootable macOS installation disk, you have to burn the DMG file to a USB drive as CD/DVD is not available for Mac computers. Here's how to do it from text commands and using a purpose-built software called WizDMG. You will first need to download the DMG file for the macOS version you wish to install. For example, if you want to create a bootable macOS Mojave installer, you will need the DMG file for macOS Mojave. Once the file has been downloaded to your PC, you can proceed with one of the bootable disk creation methods shown below.
Method 1: How to Create Bootable USB Installer for Mac via Commands
macOS (formly named Mac OS X) is just a variant of popular Unix based operating system. This means a lot of daily and advanced tasks on Mac can be done via text commands such as creating bootable USB installer for Mac. However, this could be a lot of challenges if you had no clue about commands and I suggest taking a look at the other solutions in this post to avoid messing up the computer with the wrong commands.
Step 1. Search macOS name in app store (Mojave, High Serria, EI Capitai). Click 'Get' button to download the installer image on your Mac. The downloaded file will be located in Application folder.
Step 2. When the download is completed, the installation windows opens automatically, just close the window and go to Application folder. You will find a file started Install, such as Install macOS Majave.
Step 3. Now connect an external flash drive with more than 16G free space. And backup the data in that USB drive as the installer erase all content from it. Open Disk Utility app and format the USB drive with APFS or Mac OS Extended.
Step 4. Open the Terminal app and copy-and-past the following commands to make a booatble USB installer from macOS image:
For Majove: sudo /Applications/Install macOS Mojave.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia --volume /Volumes/MyVolume
For High Serria: sudo /Applications/Install macOS High Sierra.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia --volume /Volumes/MyVolume
For EI Capitan: sudo /Applications/Install OS X El Capitan.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia --volume /Volumes/MyVolume --applicationpath /Applications/Install OS X El Capitan.app
Step 5. Input the admin password when being prompted. And wait for the booatable disk being created. When it is done successfully, you will receive a message shown in above screenshot.
Unconfortable with text commadns and prefer doing it in a simple way? The second suggestion is more user friendly!
Method 2: How to Make Bootable USB from macOS with WizDMG
WizDMG fills a huge gap in Windows not supporting DMG files. It is a desktop utility supporting Windows and Mac. It allows you to directly burn DMG files to disk in order to create a bootable macOS Mojave installer or a boot disk for any macOS version.
WizDMG offers an intuitive interface with no clutter and full functionality to handle DMG files. Apart from burning such disk image files to DVD/CD or USB, it also gives you edit options where you can add and remove files from within the DMG file, rename DMG files and even create DMGs from files and folders on your desktop. This software application has been created for novice users as well as experts. It is easy to use, has a very high burn success rate and will help you create a bootable macOS installer in no time. Follow the instructions below:

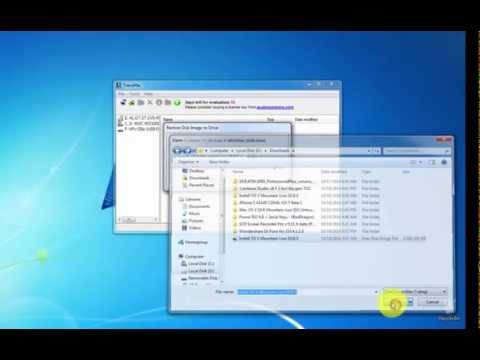
Step 1Install WizDMG
Download WizDMG from the official website and install it on your PC. Launch the program and select the 'Burn' option in the main interface.
Step 2Create Bootable USB from macOS Install Image
Create Dmg For Mac Application Form
Click on Load DMG to import the macOS installation file into the application. Insert a USB (16G free space) and click on the 'Burn' button next to the appropriate media type.
The important thing to remember here is that you now know how to create a macOS installer in Windows. There aren't a lot of options out there because of the compatibility issues between Mac and Windows environments. That means converting DMG to ISO and back again to DMG leaves the door open for corrupted files and incorrectly burned bootable media, which defeats the whole purpose because it might not even work in the end.
Method 3: Create macOS High Serria/Mojave Bootable USB on Windows 10/7
Another way to create macoS bootable disk on Windows is using a tool called DMG2IMG along with Windows command prompt. It requires a bit of a workaround, but even novice users can learn to burn a DMG file to a disk to create bootable media for a macOS installation. Just make sure you follow the instructions below carefully.
Step 1. Download DMG2IMG and install it in your Windows PC. Open File Explorer and go to the folder containing the DMG2IMG program, then right-click and select 'Open command windows here.'
Step 2. Type the following command and hit Enter: dmg2img [sourcefile.dmg] [destinationfile.iso]
Step 3. Now that the DMG file has been converted to ISO format, you can use the following command to burn it to a disk. Before that, insert a disk into the optical drive: isoburn.exe /Q E: 'C:UsersUsernameDesktopdestinationfile.iso'
Step 4. This command utilizes the Windows native disk image burner to burn the ISO to the disk in your optical drive. The ISO file can't be used directly in macOS, but it can be mounted as a virtual drive. Once you do this, you can convert it back to DMG using Disk Utility in Mac. You can then use this as your bootable macOS installer.
Create Dmg For Mac Application Download
As you can see, this is a bit of a workaround because DMG files aren't natively supported in Windows. Likewise, ISO files aren't fully supported in macOS. However, you can use this method to create a macOS installation disk in Windows. If you want a much simpler solution, then review the next method shown here.
Summary
If you ask us how to create a bootable macOS installation disk, this is the method we recommend. There's no confusing command line work involved, you don't need a bunch of additional software utilities to get the job done, and the high accuracy of the application ensures that you won't be wasting disk after disk trying to burn the installation media for macOS onto a disk. Use WizDMG as a quick and painless way to create a macOS installation disk in a very short time.